近日,课题组杜博文硕士生、高军教授及其合作单位撰写研究论文,探究了人员接触烹饪油烟后,肺功能相关、炎症相关、心血管相关和氧化应激相关生物标志物的变化,进一步阐明烹饪油烟暴露所致的健康风险。该研究的合作单位有昆士兰理工大学,复旦大学,上海市环境科学研究院和华东理工大学。该成果被Building and Environment杂志接收。这是课题组近年来再次有硕士生发表高水平SCI论文,向杜博文和高老师表示祝贺!
题目:Particle exposure level and potential health risks of domestic Chinese cooking
杂志:Building and Environment
作者:
Bowen Du1, Jun Gao*,1, Jie Chen1, Svetlana Stevanovic2, Zoran Ristovski2, Lina Wang3, Lin Wang4,Hongli Wang5, Li Li5
1School of Mechanical Engineering, Tongji University, 201804, Shanghai, China
2 Science & Engineering Faculty,Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane Area, Australia
3School of Resources and Environmental Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, Shanghai, China
4Shanghai Key Laboratory of Atmospheric Particle Pollution Prevention, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
5State Environmental Protection Key Laboratory of Formation and Prevention of Urban Air Pollution Complex, Shanghai Academy of Environmental Sciences, Shanghai 200233, China
引用:Bowen Du, Jun Gao, Jie Chen, Svetlana Stevanovic, Zoran Ristovski, Lina Wang, Lin Wang, Particle exposure level and potential health risks of domestic Chinese cooking, Building and Environment, Volume 123, October 2017, Pages 564-574, ISSN 0360-1323, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2017.07.031.
(http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S036013231730330X)
附图:
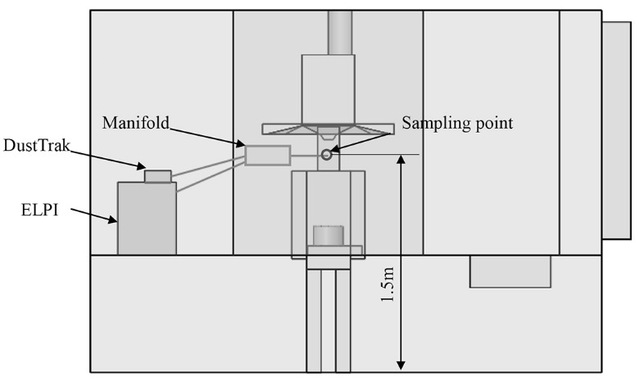
Figure.1 Laboratory layout
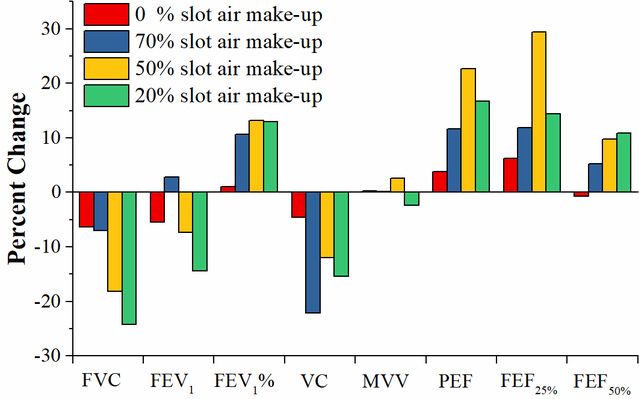
Figure 5. Percent change of lung function biomarkers after COF exposure
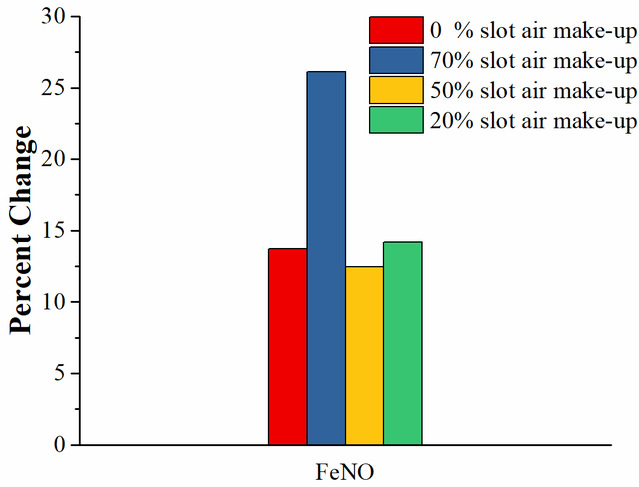
Figure 6. Percent change of FeNO after COF exposure
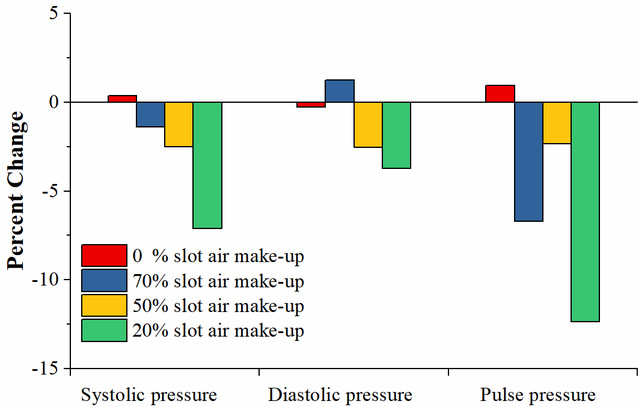
Figure 7. Percent change of blood pressure after COF exposure
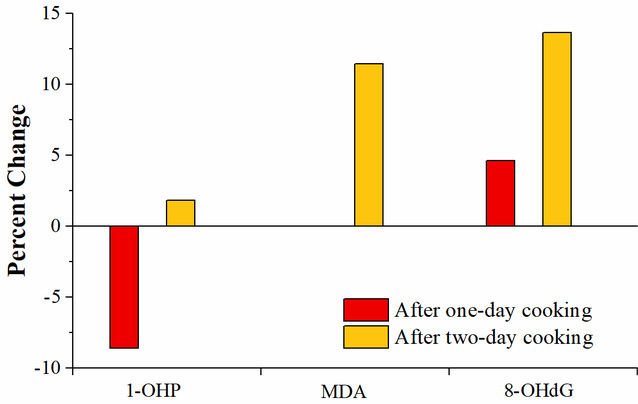
Figure 8. Percent change of oxidative stress biomarkers after COF exposure
Copyright@ 同济大学张旭教授课题组

 同济大学主页
同济大学主页